How are rainbows formed?
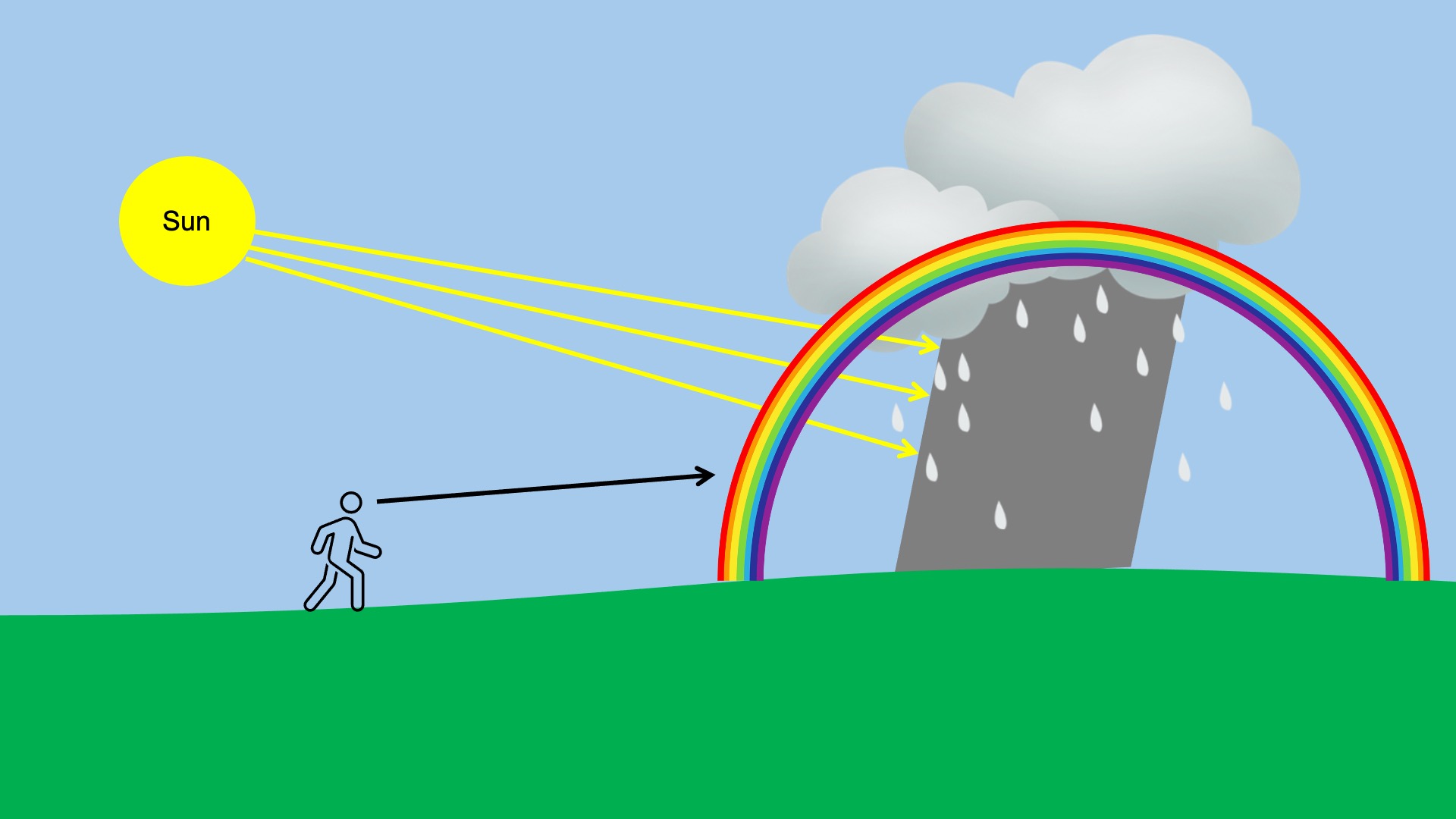
A rainbow forms when sunlight is broken down by water droplets suspended in the atmosphere, which act like a prism.
Definition
A rainbow is a photometeor: an optical phenomenon that occurs in the sky, visible in the opposite direction to the Sun when it shines during rain.
When can we see a rainbow?
We can see a rainbow when water droplets are falling or suspended in the air, usually just after it rains, and when there is a powerful light source, typically the sun, shining behind the observer. Rainbows are most visible when the sky opposite the sun is darkened because the colors stand out more against the backdrop of a dark sky.
This effect can also be seen near waterfalls or in mist when there is a light source behind you.
Color decomposition
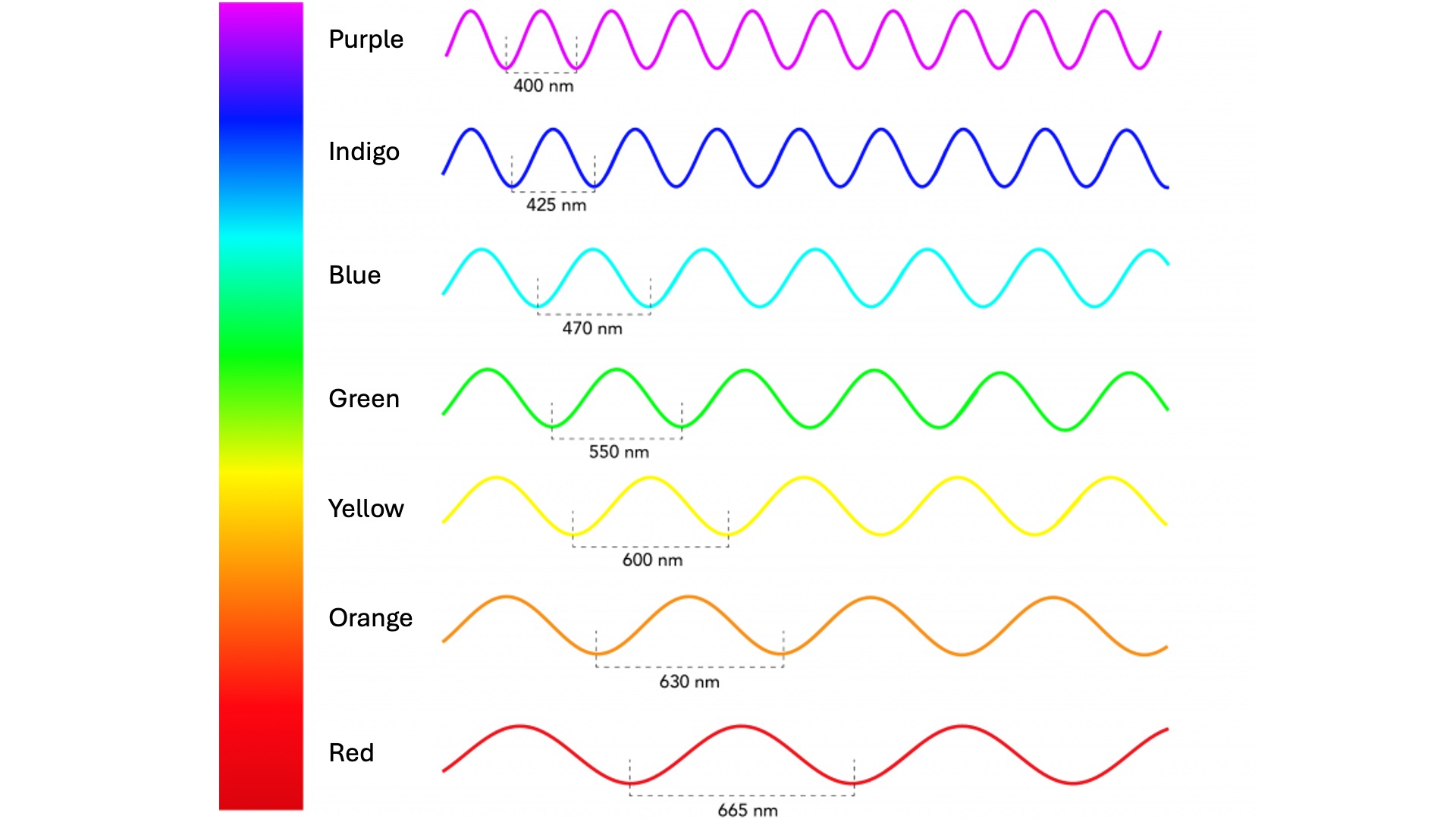
Sunlight consists of several wavelengths, or colors. When these wavelengths enter a drop of water, some bend more than others. Purple (the shortest wavelength of visible light) bends the most, while red (the longest wavelength of visible light) bends the least.
What happens inside water droplets?
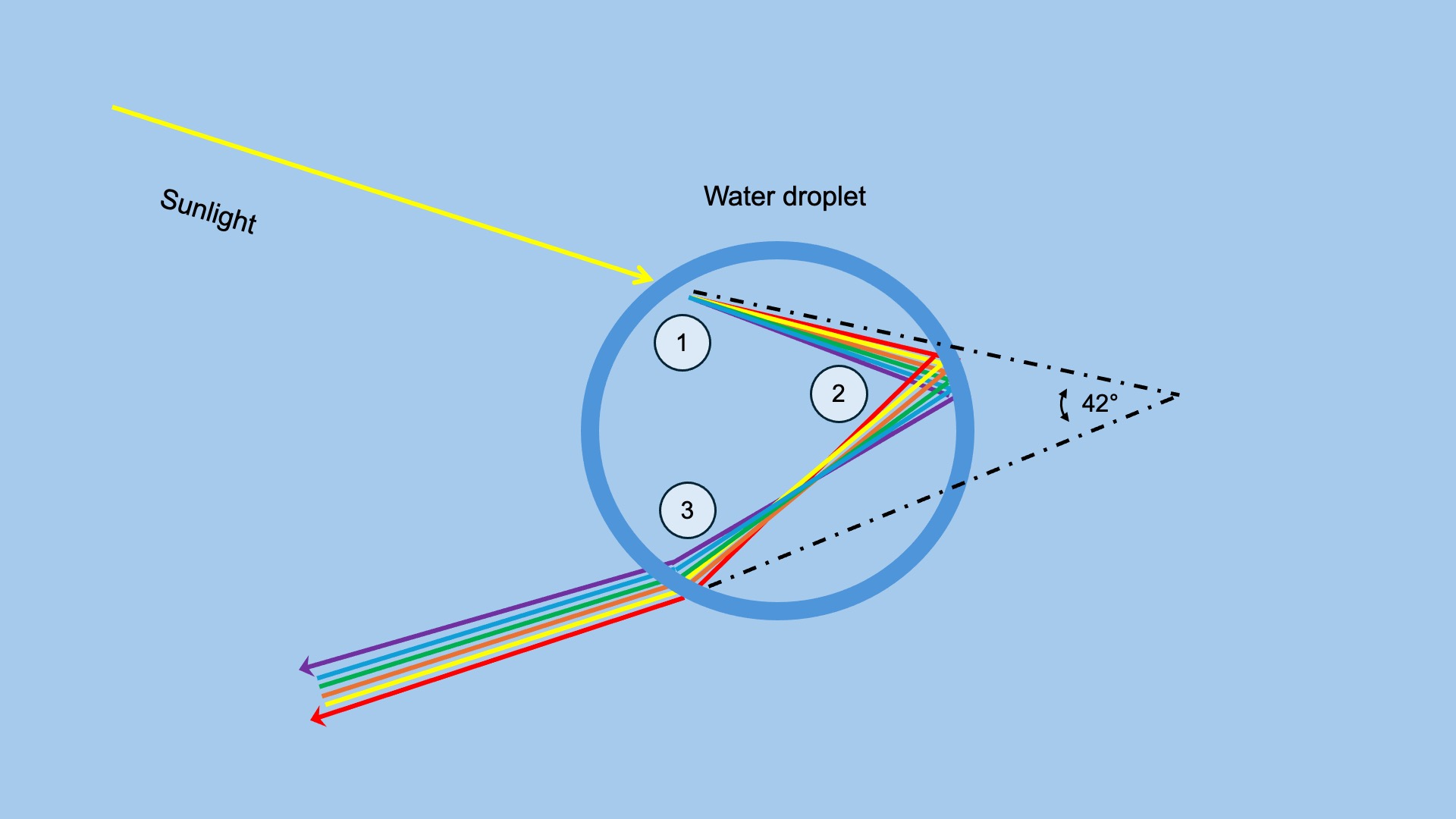
Light enters the droplet, causing an initial refraction (1) of the light ray. Due to the transition from air to water, the ray is deflected because water is denser. This breaks the ray down into wavelengths, or colors. Depending on the wavelength, or color, the angle at which the light is deflected is different. This is similar to what happens in a prism, which allows us to see the spectrum of colors.
The light then bounces off the back of the water droplet (2) and refracts again (3) as it exits the droplet. Thus, when light exits the water droplet, it is separated into all its wavelengths. Light reflected by water droplets toward an observer with the sun behind him will appear separated into all the colors of the rainbow!
What is the order of colors in the rainbow?
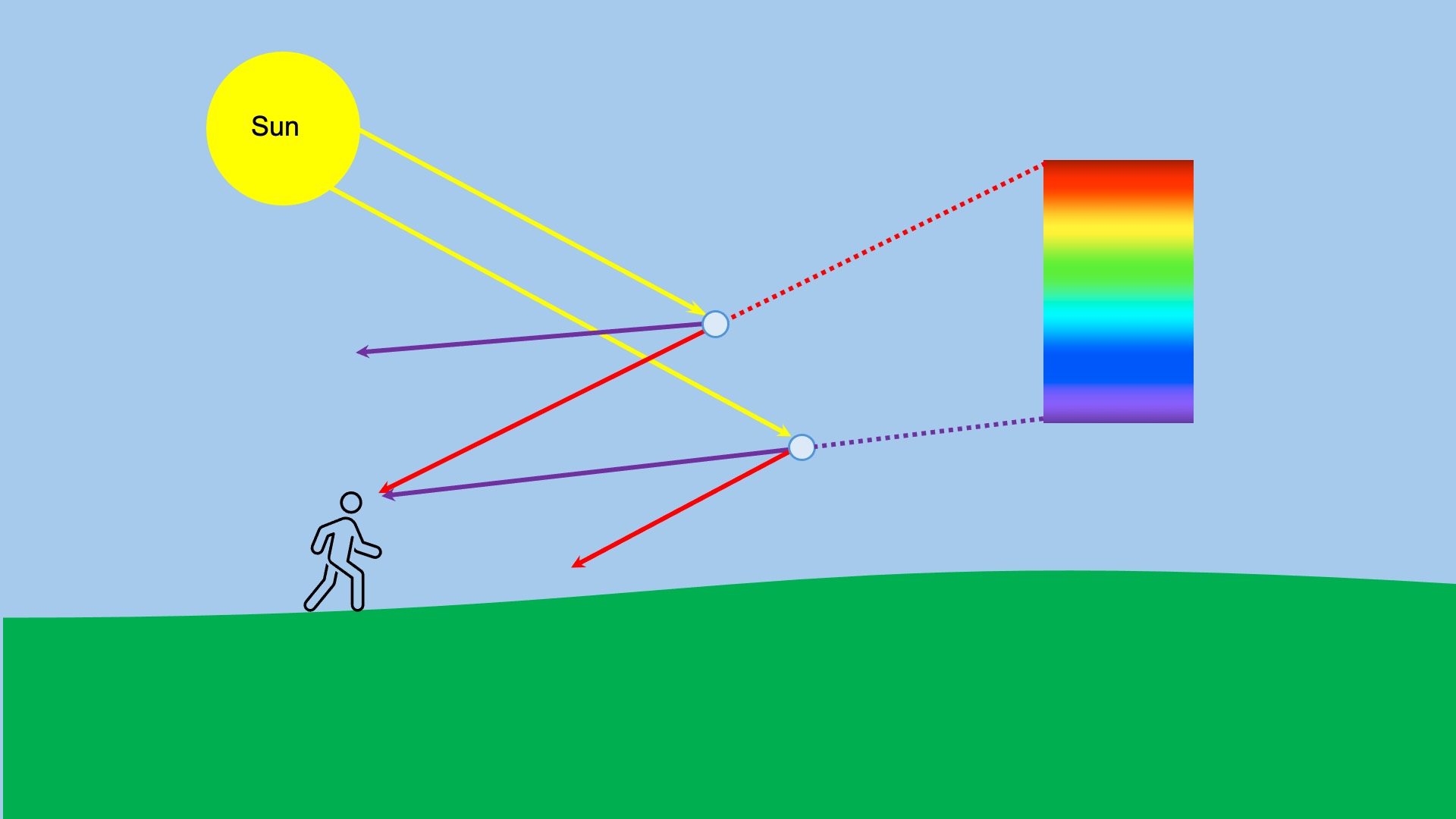
Figure 2, above, shows purple at the top of the spectrum, but in a rainbow, purple appears at the bottom. This is because the light broken down by the raindrops appears to the observer at a different angle. Red appears at the top of the rainbow, and purple appears at the bottom (Figure 3).
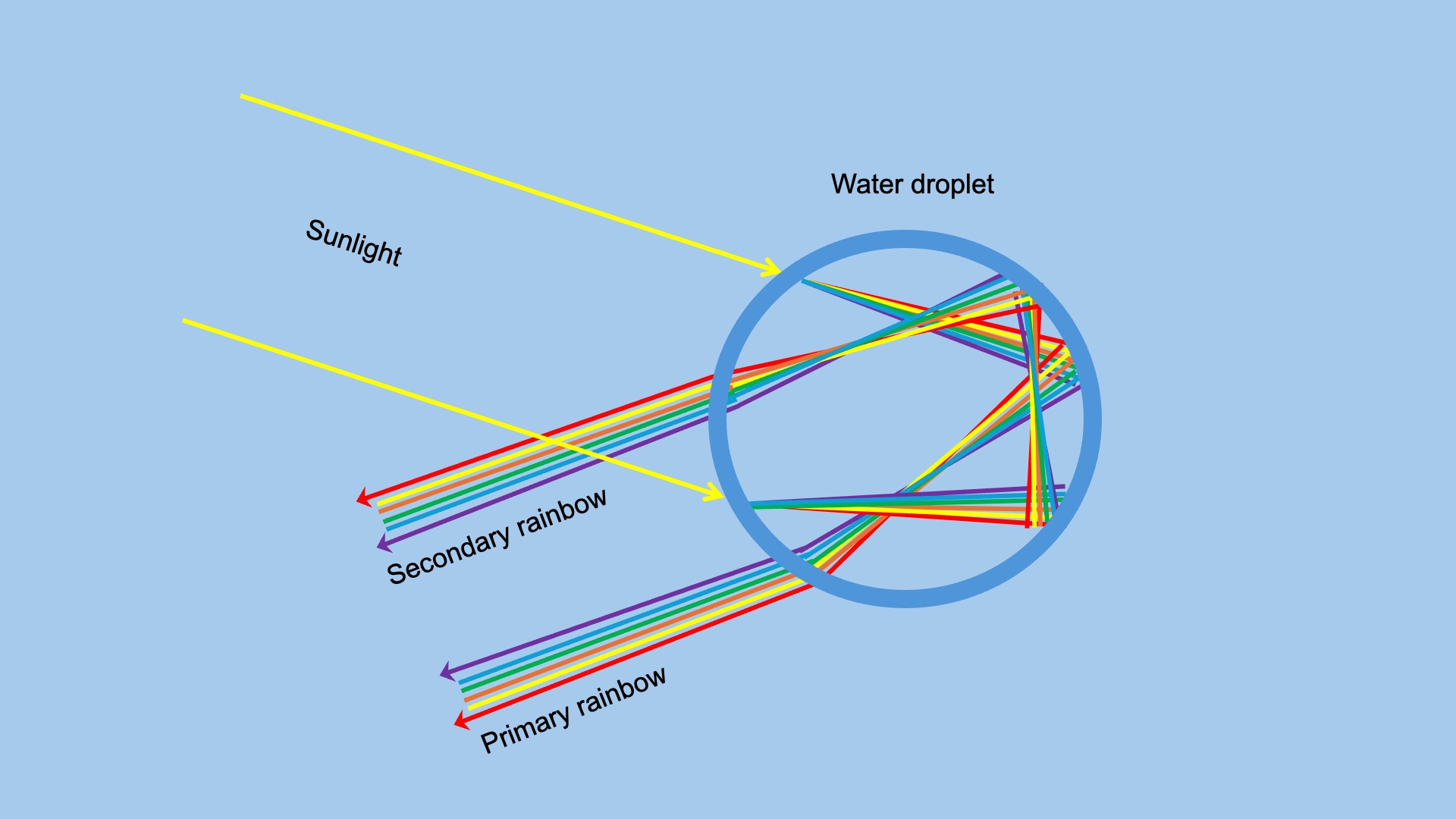
What causes a double rainbow?
A secondary rainbow forms when sunlight is reflected twice inside water droplets. Secondary rainbows are generally weaker and less visible.
Primary rainbow is caused by rays undergoing internal refraction within water droplets. The colors range from red on the outside to purple on the inside.
A secondary rainbow is caused by a second refraction inside the droplet. This "reflected" light exits the droplet at a different angle (50° instead of 42° for the primary rainbow). This is why the secondary rainbow appears above the primary rainbow. The order of colors in the secondary rainbow is reversed, with red on the inside and purple on the outside.
Why is a rainbow an arc?
A rainbow is actually a complete circle. However, our horizon limits our field of vision from the ground, preventing us from seeing the lower part of the circle. However, it is possible to see the entire circle from an airplane.
Important: To photograph a rainbow, remove your polarizing filter, otherwise, the rainbow will appear faint or not at all in your photos.